Foliage Height Diversity (FHD)¶
Theory¶
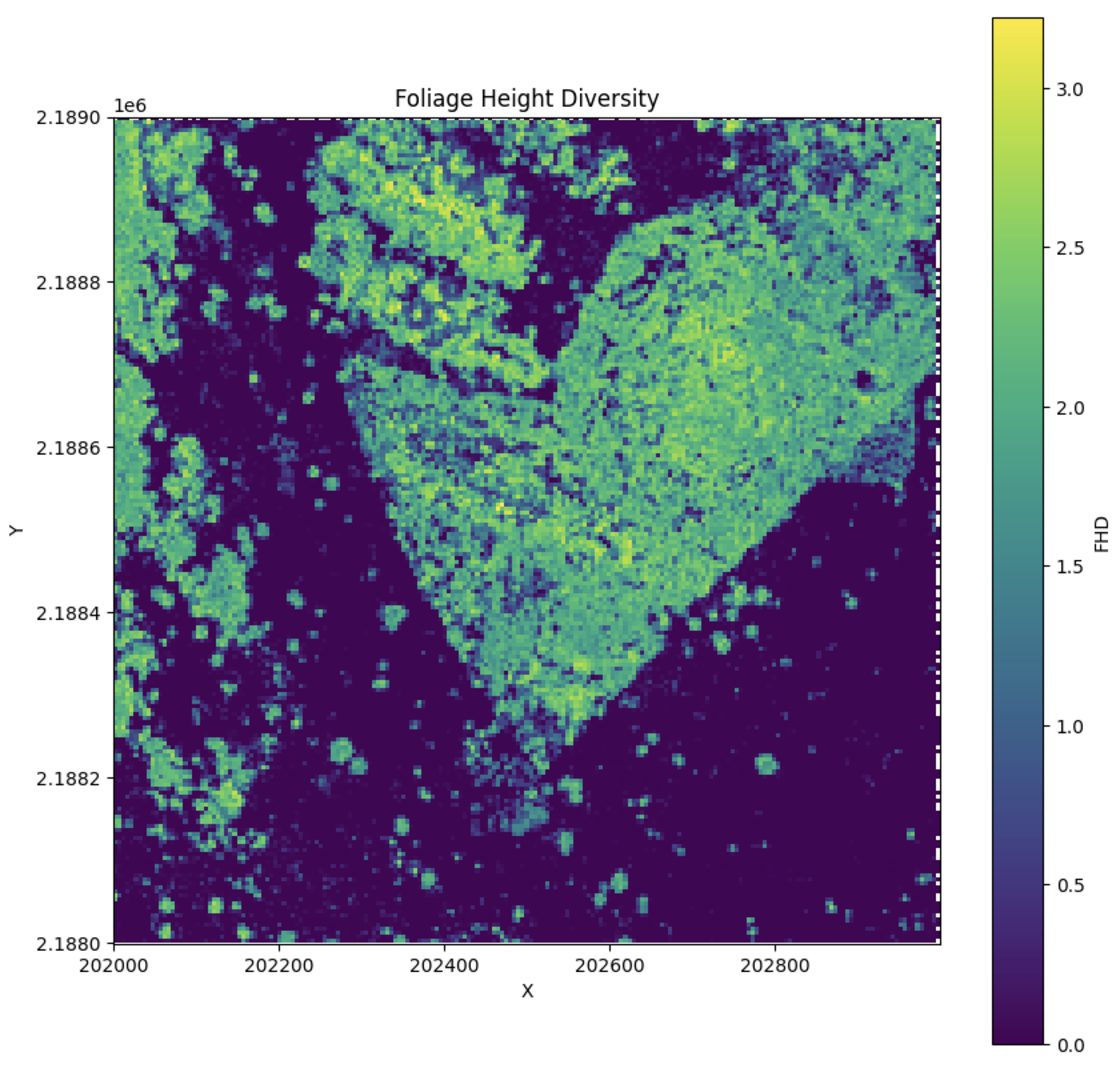
Foliage Height Diversity (FHD) is a metric that quantifies the vertical distribution of plant material in the forest canopy. It is based on Shannon entropy and calculated using methods derived from Hurlbert (1971) and MacArthur & MacArthur (1961).
Where: - \( FHD \) is the Foliage Height Diversity. - \( p_i \) is the proportion of total plant material in voxel \( i \) relative to the entire vertical column. - \( n \) is the number of vertical layers in the canopy.
FHD provides an indication of how plant material is distributed vertically, with higher values suggesting a more even distribution of foliage across different height levels.
Calculating FHD¶
To calculate FHD:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | |
Notes
- min_height defaults to 0 (all returns). Raise it (e.g., 2 m) to exclude near-ground returns from the entropy calculation.
- max_height can limit the top of the integration range if needed.
References¶
Hurlbert, Stuart H. 1971. "The Nonconcept of Species Diversity: A Critique and Alternative Parameters." Ecology 52 (4): 577--86. https://doi.org/10.2307/1934145.
MacArthur, Robert H., and John W. MacArthur. 1961. "On Bird Species Diversity." Ecology 42 (3): 594--98. https://doi.org/10.2307/1932254.